Filter Pleating Machine,Rotary Pleating,Rotary Pleater,Mini Pleat Filter Machine ChangZhou FENGJU Machinery Equipment CO., LTD , https://www.czfengjumachinery.com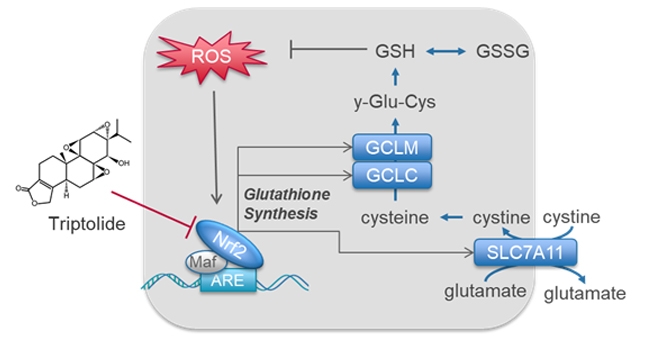
Dalian Institute of Chemical Technology and others proposed a new strategy to interfere with glutathione metabolism in the treatment of gliomas
[ Instrument R & D of Instrument Network ] Recently, Xu Guowang, a researcher of the Biomolecule High Resolution Separation Analysis and Metabolomics Research Group of the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) researcher Yang Chunzhang teamed up to dehydrogenate isocitrate New progress has been made in the treatment of enzyme 1 (IDH1) mutant gliomas, revealing the importance of Nrf2 regulated glutathione (GSH) metabolic pathways, and proposed a new strategy to intervene in glutathione metabolism to treat gliomas.
Glutathione (glutathione, r-glutamyl cysteingl + glycine, GSH) is a tripeptide containing γ-amide bond and thiol group, which is composed of glutamic acid, cysteine ​​and glycine, and exists in almost every body cell.
Glutathione can help maintain normal immune system function, and has antioxidant and integrated detoxification effects. The thiol group on cysteine ​​is its active group (so it is often abbreviated as G-SH), and it is easy to combine with certain drugs and toxins, so that it has integrated detoxification effect. Glutathione can be used not only as a medicine but also as a base material for functional foods, and is widely used in functional foods such as anti-aging, enhancing immunity and anti-tumor.
Glutathione comes in two forms: reduced (G-SH) and oxidized (GSSG). Under physiological conditions, reduced glutathione accounts for the vast majority. Glutathione reductase can catalyze the interconversion between the two types, and the coenzyme of this enzyme can also provide NADPH for pentose phosphate bypass metabolism.
Glioma is a primary brain tumor, IDH1 mutation is a common pathogenic mutation, but currently there is a lack of selective treatment for IDH1 mutant glioma. In response to this problem, the research team found that in IDH1 mutant cancer cells, the glutathione anabolic pathway is very active. Glutathione anabolism is regulated by Nrf2 transcription factor and is an important antioxidant metabolic pathway. In vitro studies have found that inhibiting the transcriptional activity of Nrf2 can reduce the synthesis of glutathione, thereby causing the apoptosis of IDH1 mutant cancer cells. Based on this finding, the research team proposed a new strategy for inhibiting the glutathione metabolic pathway to treat IDH1 mutant glioma.
Tripterygium wilfordii, also known as triptolide, triptolide, is an epoxy diterpene lactone compound extracted from the roots, leaves, flowers and fruits of Tripterygium wilfordii plant. Alkaloids such as vinegarine, tripterygium wilfordine, tripterygium wilfordine, tripterygium wilfordii, and tripterygium wilfordine constitute the main active ingredients of tripterygium wilfordii extract, which is insoluble in water, and soluble in methanol and dimethyl Sulfoxide, absolute ethanol, ethyl acetate, etc. Has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects.
Triptolide is a diterpene epoxy compound extracted from Tripterygium wilfordii, which is a highly effective Nrf2 inhibitor. In vitro and in vivo models, it was found that in the IDH1 mutant glioma cells intervened by triptolide, the transcriptional activity of Nrf2 was inhibited, and the expressions of GCLC, GCLM and SLC7A11 were down-regulated, thereby disrupting the metabolism of glutathione. The increased oxidative damage leads to apoptosis. This study illustrates the importance of inhibiting the glutathione metabolic pathway regulated by Nrf2 for tumor therapy, and at the same time provides a new idea for the treatment of malignant tumors with IDH1 mutations.